This is a experiment of Information Security, about 7 exercises in this blog. May be a lot mistakes here, if you find it, please contact me. This lab consists of three parts:
Lab 3 : Privilege Separation
Lab Environment Setup
- Platform : Ubuntu 12.04 ( 64 bits )
- Contents : Privilege Separation
Brief introduction
This lab consists of three parts:
- Part A: you will examine the architecture of the Touchstone web server. The Touchstone web server in this lab differs dramatically from those from lab 1 and 2, the current one is based on the idea of services;
- Part B: you will explore jail, by which you can constraint the service in some fake root directory; and
- Part C: you will privilege-separate the Touchstone web server by assigning each component appropriate privilege.
Part A: The Touchstone Web Server
Exercise 1.
In order to gain deeper understanding of the internal architecture of the Touchstone web server, let’s use gdb to debug the banksv service.First, launch the server:
1 | $ sudo ./touchstone |
now use gdb to attach to the banksv service:
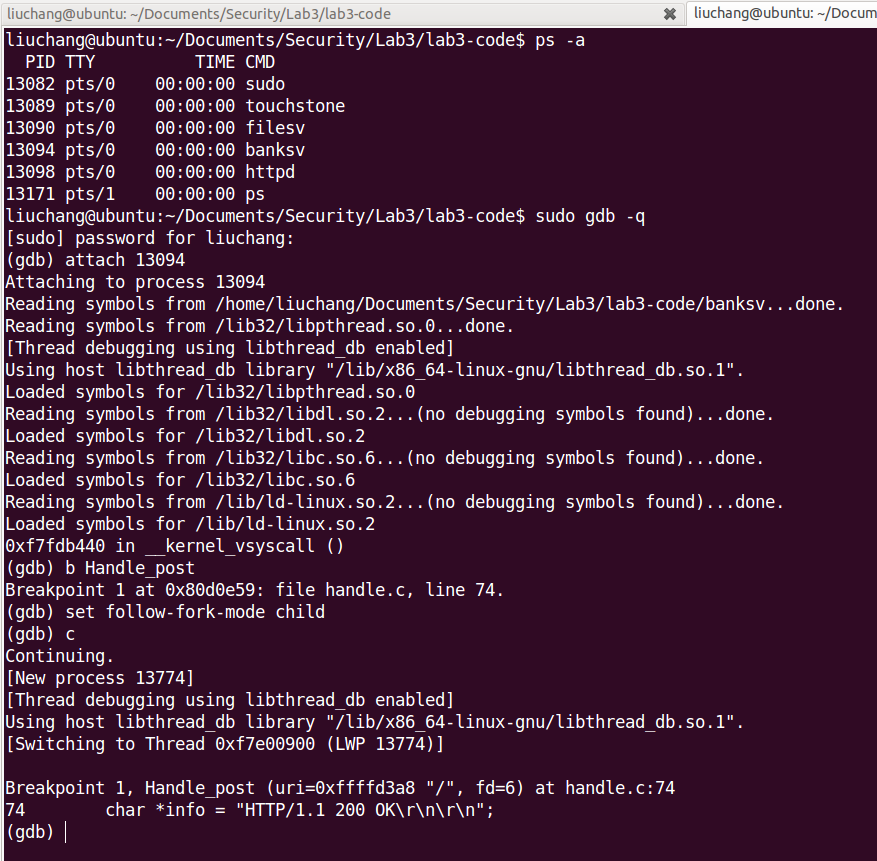
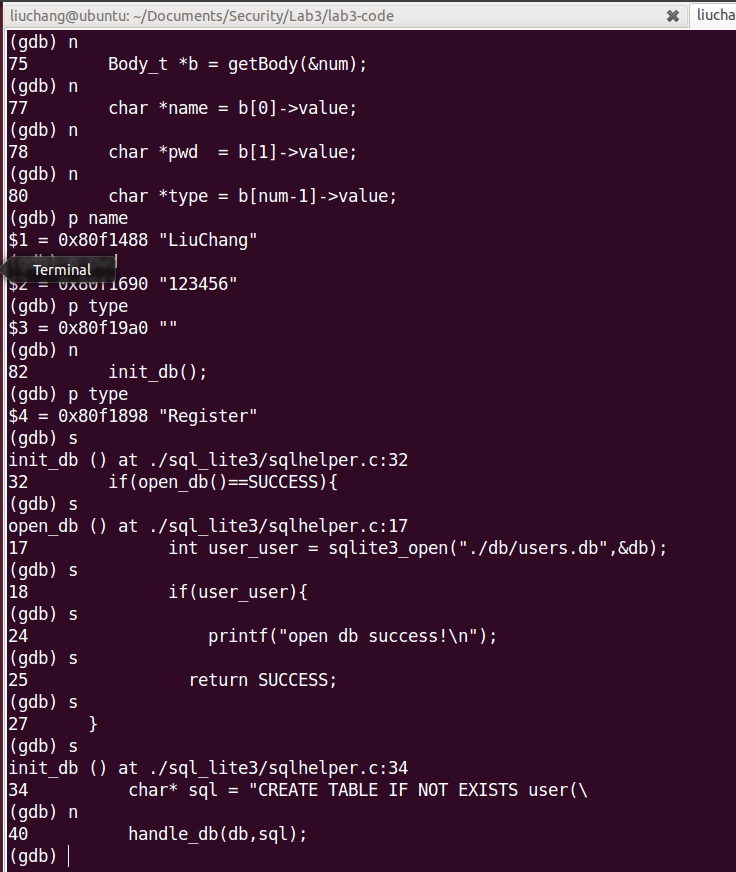
Exercise 2.
Finally, you will write some code. Extend the current sqlite3 user table, to add more information. For instance, you can add time and IP address to the user table, so that when one user has logged in, the web page can display the last login time, the current login address, etc… You may want to read some sqlite3 documentations.
In order to complete these functions, I made effort in two places. One is to pass the value of client_addr, the other is to modify the user’s database.
Firstly, we pass the value of client_addr to httpd process though by executing write( disp_fds[1], inet_ntoa(client_addr), 50 ). And in httpd process, as a hub, we receive this value. Then we send this value to filesv and banksv processes respectively according to pipefd descriptor. So that, we can process this address to the browser. Why we don’t send it to filesv and banksv directly ? It is just a pity that the server has shut down these descriptors before new client coming…
Secondly, we should add additional fields for the user table. One is the ip_addr, the other is last_time(which can record the last login time). Before modifying user table, we should drop it because some datas has existed in the user table. In order to get and update the last login time and last ip address, two functions need to be implemented. As follows :
1 | void getLastState(const char * u_name, const char * u_passwd, char * last_ip_addr, char * last_time) { |
GET …/…/…/…/…/…/…/…/…/…/…/etc/shadow HTTP/1.1\r\n\r\n
1 | and sent it, some funny things happened... |
Now re-do exercise 3 to visit the file /etc/passwd. If your chroot protection works, your browser will behave like this (leaking no sensitive information): As follows:
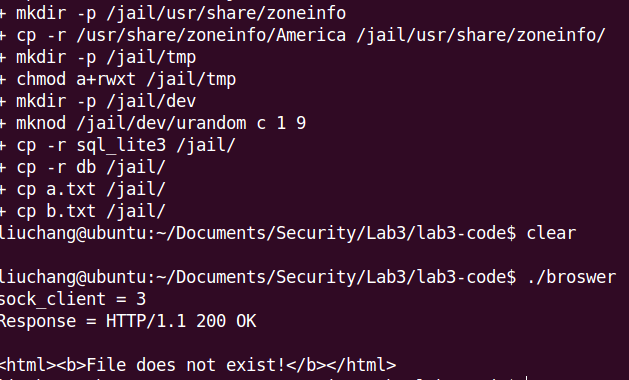
The principle of this method is to exclude some important datas, and run in a restricted environment. For example, in chroot-setup.h file, we don’t copy some important files(passwd,shadow) to the /jail/etc/.
Part C: Privilege Separation
Exercise 5.
Modify your browser code to inject some shell code the server. Your shell code attack the httpd daemon and unlink the file /db/users.db. Using ret-to-libc attack can make this a little simpler.
Just likes the [Lab2], we can complete it in the same way. And then I will illustrate it detailed in a picture and attach my codes later…
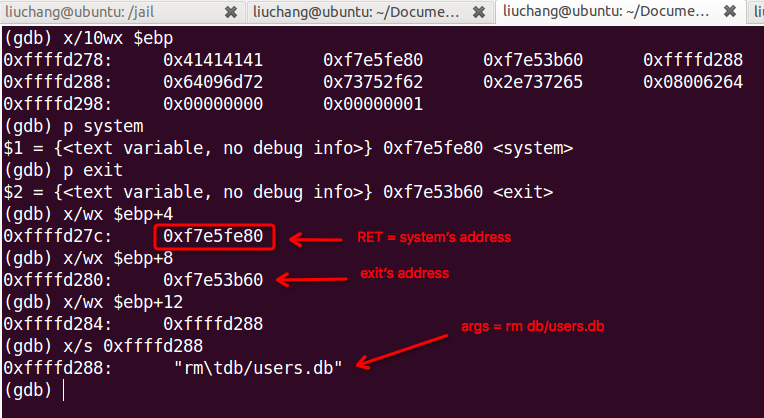
1 |
|
Exercise 6.
Modify the function in the file server.c , to set up the user and group IDs properly when services are launched. Think carefully about how your code can set the user and group IDs by setresuid()、setgroups()、setresgid().
Set file and directory permissions to ensure that the static service cannot read the database files from the dynamic service, and vice versa. Try to modify the chroot-setup.sh to set the permission for different files.
In order to bind port 80 for the touchstone program, we have to start this server as a root. However, in the server.c file, we use fork and execve to run the filesv httpd banksv programs, as a result, these new programs will own root privilege…It is too dangerous…
To solve this program, we need separate their permissions carefully.
Firstly, when to execve these new processes, we need to use setresuid to change their permissions respectively. Just as follows:
Before executing filesv:
1 | setresuid(115,115,115); |
Before executing banksv httpd:
1 | setresuid(1000, 1000, 1000); |
Secondly, we modify the chroot-setup.sh and change the db directory to be owned by liuchang. After that, some important files need to be reassigned permissions. I will attach my codes later.
1 | chown -R liuchang:liuchang /jail/db |
When we construct a HTTP request likes ‘GET db/users.db’ or ‘GET /etc/shadow’, “FILE not existed” and ‘permissions deny’ errors will be returned. Just like this :
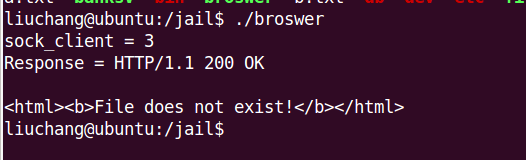
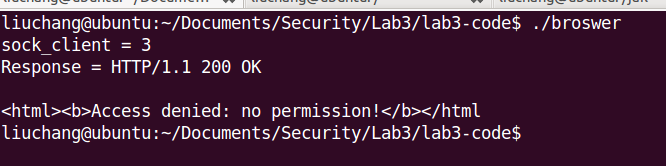
Exercise 7.
Is it is possible to perform a buffer overflow attack as lab1? Why?
Of course, it does. The httpd filesv banksv processes will call getToken function to parse HTTP requests, however, getToken is vulnerable and can be exploited easily. Privilege separation can deny some illegal requests rather than preventing these programs from Buffer Overflow Attack. So it is possible to perform a buffer overflow attack unless we fixed up this hole…
Challenge! Capture The Flag!!!
Now we provide you a simple CTF game, download the file, and use what you can do to reverse it, finally you should find the flag.
Also, we strip the [file] as what Mr.H did in the last class. So you may need use gdb to debug it. May following three commands is useful:
1 | (gdb)layout asm |
And you should know that, who will invoke the main function. CAUTION: the flag is generated randomly, so any cheat will be found easily:
I capture the flag by using IDA Pro tool… It is a little awkward… As we know, IDA is a professional weapon to disassember programs. We can see more details based on it. In this game, we use it to analysis this program and find something in the .data section, as a picture shown :
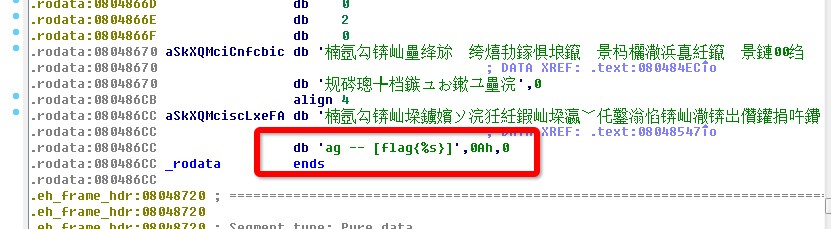
Then we begin to look for which function will refer this data.
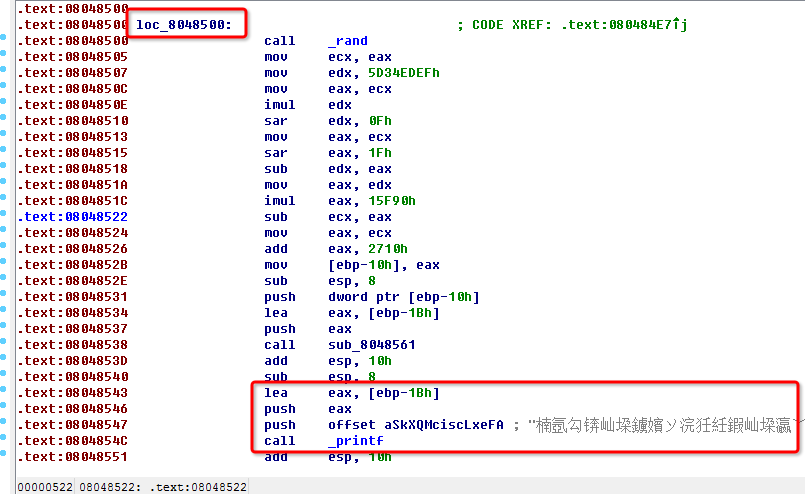
The function named loc_8048500 will use this data. After that, we should follow flow of this program’s execution, and try to find how can invoke this function. Fortunately, I make it. As shown in a picture, we can find it absolutely though by
objdum -d reverse | grep 8048500
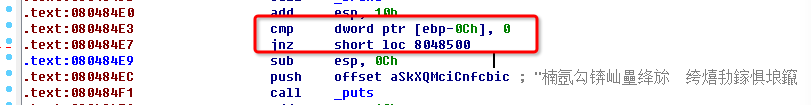
That means when $ebp-12 is not equal to $0, the function will be called. OK ! Let’s try it in GDB.
Firstly, we can break point in __libc_main_start and srand( We can get that funtion more quickly. I found it for a long time…555555…). Then type ‘r’ and ‘layout asm’ to watch the assember instructions. And type ‘si’ to follow this program until arriving here as follows :
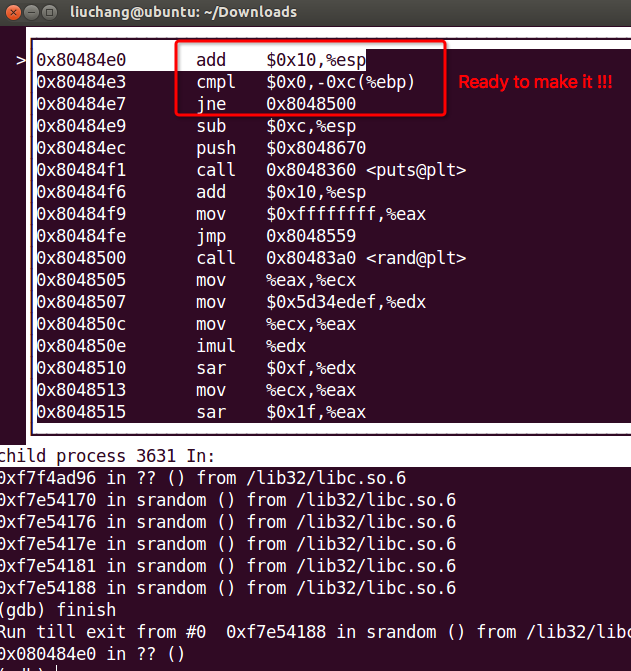
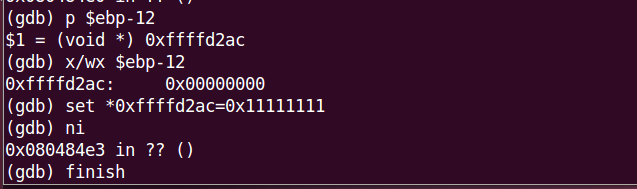
High tide !!! We are going to change the $ebp-12. Like this :
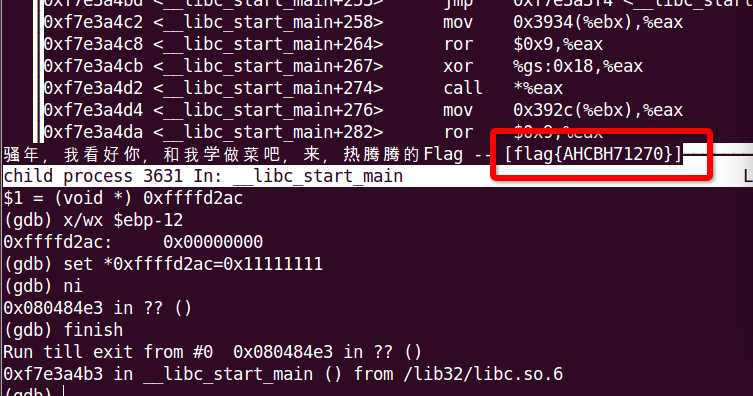
Finally, we can get the flag as follows :
An important note in the end:
- We can not set the value directly ( eg. set $ebp-12 = 0x11111111 ).
- We can type ‘finish’ when we want to end the funtion call quickly. It will reduce our time.